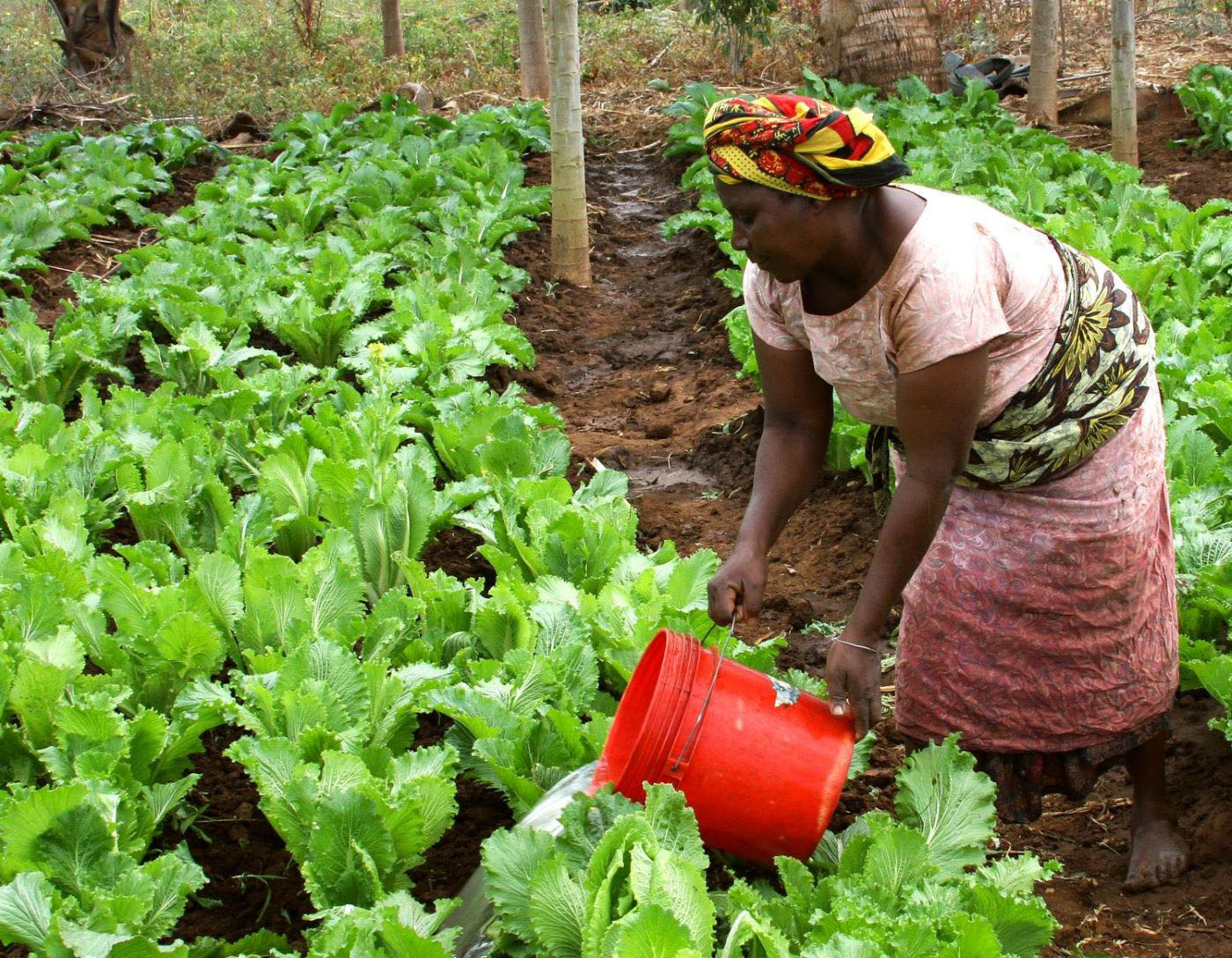
The World Food Programme has world-class logistics, but its ability to manage financial risk is extremely limited. The WFP procures 100 percent of its food through spot markets, which subjects it to substantial commodity and transport price risks and significant delays delivering food. Relying on reactive emergency appeals and on donors that tend to earmark contributions and make commitments one year at a time only adds to operational inflexibility and uncertainty.
On the other hand, much of the WFP’s operations are fairly predictable, especially the countries served and the volume of food delivered. The Programme should consider implementing a targeted hedging pilot strategy focused on several chronically food vulnerable countries. Several risk-management instruments are available, such as physical call options, forward contracts, and futures contracts. Key benefits of such hedging strategies would include greater financial predictability, the potential for improved delivery times, and increased local and regional trade that could build on the WFP’s Purchase for Progress initiative.
Changes from donors would also help the WFP shore up its operations. Greater commitments of untied cash donations from the United States and other major donors can provide the WFP significant operational flexibility to execute prudent financial management operations. Donor contributions to the proposed Food Security Trust Fund at the World Bank would further support WFP hedging operations. This fund could provide a financial guarantee or modest credit line which would enable the WFP to enter into commodity derivative contracts for up to one year in the future.
Preview
Rights & Permissions
You may use and disseminate CGD’s publications under these conditions.